В условиях стремительного развития информационных технологий строительство и обслуживание центров обработки данных сталкиваются с растущими трудностями. В частности, эффективное и энергоэффективное охлаждение стало ключевым аспектом работы центров обработки данных. В настоящее время системы жидкостного охлаждения и системы прецизионного кондиционирования воздуха являются двумя наиболее распространёнными технологиями охлаждения, используемыми в центрах обработки данных, каждая из которых разработана для удовлетворения специфических потребностей в охлаждении высокоплотной ИТ-инфраструктуры. В этой статье будут подробно рассмотрены определения и различия между этими двумя технологиями, а также значительные преимущества систем жидкостного охлаждения с точки зрения эффективности охлаждения, энергопотребления и использования пространства, что поможет предприятиям выбрать оптимальное решение для охлаждения.
1. Определение прецизионных систем кондиционирования воздуха
Прецизионные системы кондиционирования воздуха Обычно используются в центрах обработки данных для контроля температуры и влажности. Эти системы используют хладагенты для поглощения тепла, выделяемого оборудованием внутри центра обработки данных. Кондиционеры обеспечивают циркуляцию охлажденного воздуха по всему помещению, удаляя нагретый воздух и поддерживая стабильную температуру и влажность в центре обработки данных. Этот процесс обеспечивает оптимальные условия работы ИТ-оборудования.
2. Определение центров обработки данных с жидкостным охлаждением
Центры обработки данных с жидкостным охлаждением В качестве охлаждающей среды используется жидкость. Хладагент протекает вблизи оборудования или непосредственно с ним, поглощая тепло и рассеивая его через чиллеры. Системы жидкостного охлаждения подразделяются на системы прямого и косвенного охлаждения. При прямом жидкостном охлаждении жидкость непосредственно контактирует с источниками тепла, такими как процессоры и графические процессоры, в то время как при косвенном жидкостном охлаждении тепло от жидкости передаётся другим системам охлаждения через теплообменник.
Различия между центрами обработки данных с жидкостным охлаждением и традиционными системами кондиционирования воздуха
3.1 Методы охлаждения
Традиционные системы кондиционирования воздуха, хотя и широко используются во многих отраслях, менее эффективны для крупных центров обработки данных, где требуются специализированные решения для охлаждения, способные справляться с высокими тепловыми нагрузками и поддерживать точный климат-контроль. Эти системы используют циркуляцию воздуха для отвода тепла. Они работают за счёт хладагентов, которые поглощают тепло из воздуха, охлаждая его перед возвратом обратно в центр обработки данных. Горячий воздух выводится из помещения, а холодный циркулирует для поддержания стабильной температуры.
В отличие от этого, в центрах обработки данных с жидкостным охлаждением используется жидкая среда (например, вода или специальные хладагенты) для непосредственного поглощения и отвода тепла от оборудования. Затем жидкость переносит тепло в охлаждающий агрегат или чиллер для рассеивания. Благодаря более высокой теплоёмкости жидкостей по сравнению с воздухом, системы жидкостного охлаждения более эффективны в передаче тепла, требуя меньшего объёма для отвода того же количества тепла.
3.2 Потребление энергии
Традиционные системы кондиционирования воздуха потребляют значительное количество энергии из-за необходимости использования мощных вентиляторов и компрессоров, обеспечивающих циркуляцию воздуха и поддержание низкой температуры. В крупных центрах обработки данных системы кондиционирования воздуха часто являются одними из самых энергозатратных, поскольку им требуется значительная электроэнергия для отвода тепла, выделяемого оборудованием.
Однако системы жидкостного охлаждения, как правило, более энергоэффективны. Поскольку жидкости эффективнее поглощают и передают тепло, чем воздух, им обычно требуется меньше энергии для поддержания стабильной температуры. Это снижает потребность в мощных вентиляторах и компрессорах, делая жидкостное охлаждение более энергоэффективным решением, особенно для установок с высокой плотностью размещения, где системы кондиционирования могут не справляться с нагрузкой.
3.3 Занятость пространства
Традиционные системы кондиционирования воздуха требуют больших блоков, воздуховодов и воздухообрабатывающих установок для управления потоками воздуха в центре обработки данных. Эти системы занимают значительное пространство, особенно в крупных центрах обработки данных, где для поддержания заданной температуры требуется несколько блоков. Необходимость в обширных воздуховодах и охлаждающих устройствах может снизить гибкость проектирования и компоновки центра обработки данных.
С другой стороны, центры обработки данных с жидкостным охлаждением могут быть более компактными. Поскольку системы жидкостного охлаждения более эффективны в передаче тепла, для них часто требуются блоки меньшего размера, более тесно интегрированные с оборудованием. Это приводит к уменьшению требований к пространству, необходимому для инфраструктуры охлаждения, что позволяет более эффективно использовать пространство и обеспечивает большую гибкость при проектировании и организации центра обработки данных.
4. Преимущества центров обработки данных с жидкостным охлаждением
4.1 Повышение эффективности охлаждения
Системы жидкостного охлаждения обеспечивают значительно более высокую эффективность теплообмена, чем системы с воздушным охлаждением. Жидкость обладает значительно большей теплоёмкостью, чем воздух. Поэтому при одинаковых условиях эксплуатации жидкостное охлаждение может эффективно отводить тепло, поддерживая стабильную температуру оборудования. Это означает, что центры обработки данных с жидкостным охлаждением могут поддерживать более высокую эффективность в средах с высокой плотностью и высокой нагрузкой.
4.2 Снижение потребления энергии
Технология жидкостного охлаждения может значительно снизить общее энергопотребление центра обработки данных. Традиционные системы кондиционирования и охлаждения часто потребляют значительное количество электроэнергии для работы вентиляторов и компрессоров, но высокая эффективность систем жидкостного охлаждения снижает это ненужное потребление энергии. В связи с ростом цен на электроэнергию и растущим вниманием к защите окружающей среды во всем мире, центры обработки данных с жидкостным охлаждением становятся предпочтительным вариантом для энергосбережения и сокращения выбросов.
4.3 Повышенная надежность и долговечность
Системы жидкостного охлаждения, благодаря непосредственному контакту с источником охлаждения, эффективно предотвращают воздействие пыли и загрязнений, находящихся в воздухе, на оборудование, снижая вероятность его выхода из строя. В традиционных системах кондиционирования воздуха, напротив, загрязняющие частицы часто оседают на оборудовании, что приводит к ухудшению теплоотвода и нарушает нормальную работу. Более того, благодаря своей относительно закрытой структуре, системы жидкостного охлаждения могут эффективно работать даже в экстремальных условиях, например, при высокой температуре и влажности.
4.4 Экологичность
Центры обработки данных с жидкостным охлаждением обеспечивают более высокие экологические преимущества по сравнению с традиционными системами кондиционирования воздуха. Системы жидкостного охлаждения обеспечивают более высокую энергоэффективность, снижая выбросы углекислого газа и негативное воздействие на окружающую среду. Кроме того, технология жидкостного охлаждения может снизить зависимость от внешних источников энергии в некоторых экстремальных климатических условиях, способствуя устойчивому развитию центров обработки данных в различных регионах.
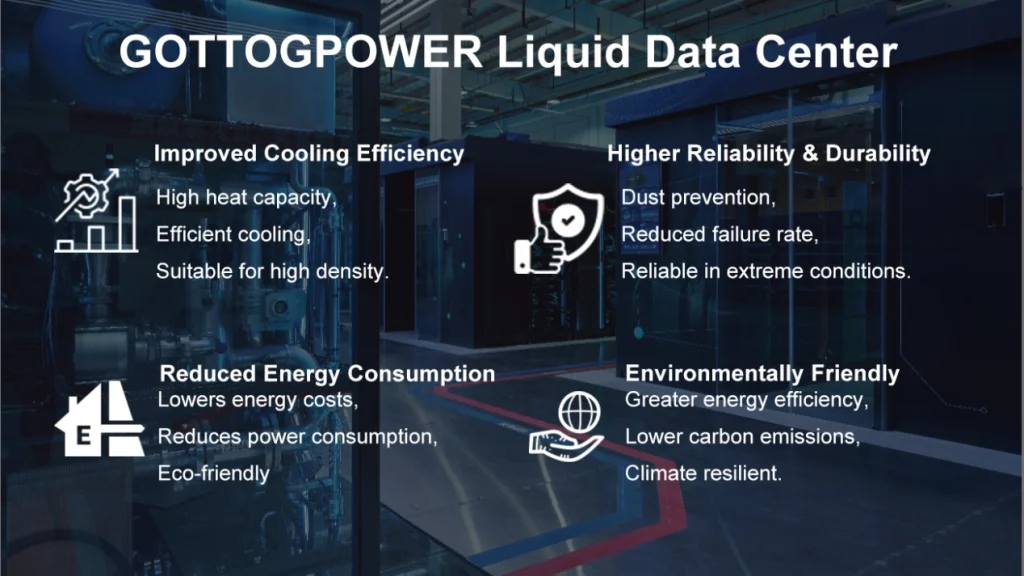
Серверные стойки с жидкостным охлаждением демонстрируют значительные преимущества в эффективности охлаждения, энергопотреблении, экономии пространства и надежности оборудования. Несмотря на более высокие первоначальные инвестиции, долгосрочные преимущества в плане энергосбережения и защиты окружающей среды весьма существенны. Для удовлетворения растущих потребностей будущих центров обработки данных технология жидкостного охлаждения, несомненно, является более экологичным вариантом. Будучи ведущим поставщиком решений в области охлаждения, GOTTOGPOWER стремится предоставлять более эффективные и энергосберегающие системы охлаждения для глобальных центров обработки данных с помощью своей инновационной технологии жидкостного охлаждения, способствуя развитию экологичных вычислений.







